Apple’s Battery Recycling Journey: From Closed Loop to Circular Economy
Related Articles
- Apple’s Strategy For 6G: What It Means For The Future Of Connectivity
- Apple’s Streaming Ambitions: A Deep Dive Into The 2024 Playbook
- How Apple’s M3 Chip Changes The Laptop Landscape In 2024: A New Era Of Performance And Efficiency
- Apple In The City: Exploring The Tech Giant’s Role In Smart City Development
- The Future Of Apple’s R&D: What’s Next After M3?
Introduction
Let’s dive straight into Apple’s Battery Recycling Journey: From Closed Loop to Circular Economy and explore the features and details you shouldn’t miss.
Video about
Apple’s Battery Recycling Journey: From Closed Loop to Circular Economy
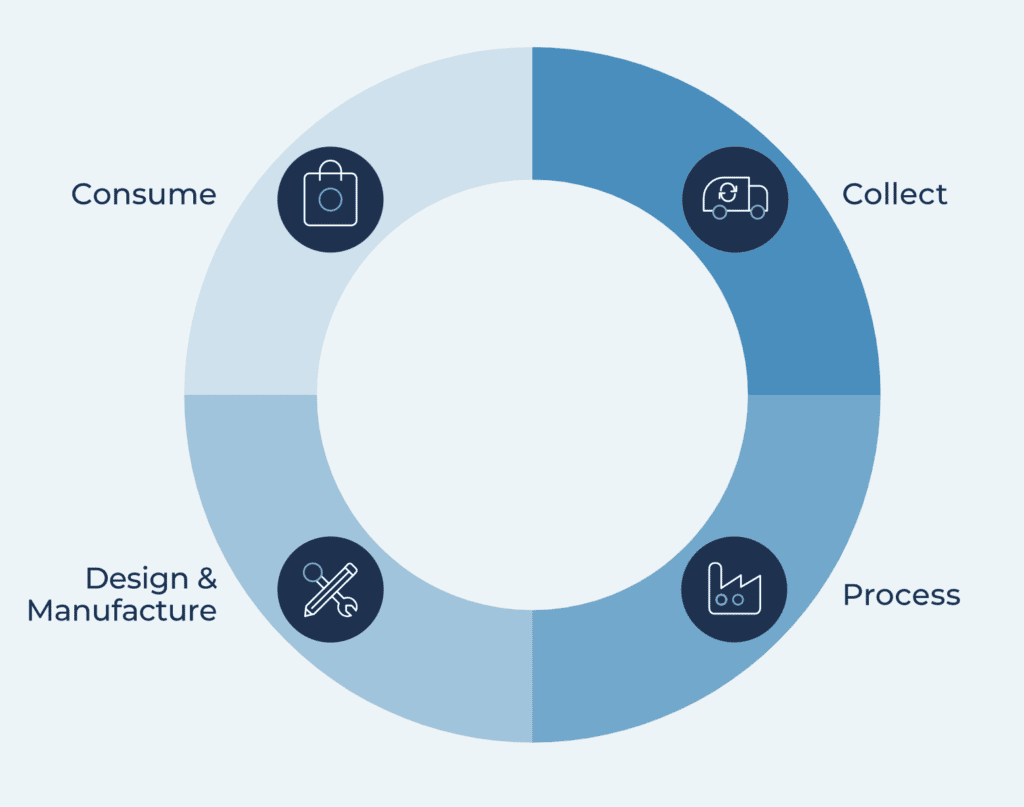
The world is awash in discarded electronics, and within those devices lie valuable materials, including lithium-ion batteries. These batteries power our smartphones, laptops, and electric vehicles, but their disposal presents a complex environmental challenge. As the demand for these devices surges, so too does the need for sustainable solutions. Apple, a company renowned for its design and innovation, has taken a proactive approach to battery recycling, aiming to minimize its environmental footprint and contribute to a more circular economy.
This article delves into Apple’s strategic evolution in battery recycling, exploring the company’s journey from a closed-loop system to a broader commitment to circularity. We’ll examine the key milestones, innovative technologies, and partnerships that have shaped Apple’s approach, highlighting the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead.
The Dawn of Apple’s Recycling Efforts: A Closed-Loop Approach
Apple’s early foray into recycling was driven by a desire to reclaim valuable materials from its own products. This "closed-loop" approach, implemented in the early 2000s, focused on recovering components like gold, silver, and platinum from discarded iPhones and iPods. The company established a network of recycling facilities and partnered with reputable recyclers to process these materials, aiming to minimize waste and maximize resource recovery.
Key Highlights:
- 2005: Apple launches its first recycling program, allowing customers to return their old devices for responsible disposal.
- 2008: Apple introduces its "closed-loop" recycling program, focusing on reclaiming valuable materials from its own products.
- 2011: Apple partners with specialized recycling companies to enhance its recycling capabilities and increase material recovery rates.

This initial phase of Apple’s recycling journey laid the foundation for its subsequent efforts. The company recognized the importance of responsible waste management and began to develop a more comprehensive approach to sustainability.
Expanding Horizons: Beyond Closed Loop and Towards Circularity
As Apple’s product portfolio expanded and the demand for lithium-ion batteries surged, the company realized that a closed-loop system alone was insufficient. The need to address the broader environmental impact of battery production and disposal became apparent. This realization marked a significant shift in Apple’s strategy, moving beyond its closed-loop system and embracing a more circular approach.
Key Highlights:
- 2013: Apple unveils its "Daisy," a robotic disassembly system designed to efficiently dismantle iPhones and recover valuable components.
- 2016: Apple partners with the World Wildlife Fund (WWF) to promote responsible cobalt sourcing for its batteries.
- 2018: Apple launches its "Liam" robot, an advanced disassembly system capable of separating and recovering key components from iPhones, including batteries.
These initiatives demonstrated Apple’s commitment to tackling the challenges associated with lithium-ion battery recycling. The company recognized the need to innovate and collaborate with partners to develop more efficient and environmentally friendly solutions.
The Rise of Innovation: Technological Advancements in Battery Recycling
Apple’s commitment to circularity has been fueled by a continuous pursuit of technological innovation. The company has invested heavily in research and development, leading to the creation of cutting-edge recycling technologies that enhance material recovery rates and minimize environmental impact.
Key Highlights:
- Daisy: This robotic disassembly system, introduced in 2013, revolutionized iPhone recycling. Daisy can efficiently dismantle iPhones, separating components and recovering valuable materials with precision.
- Liam: In 2018, Apple unveiled Liam, an even more advanced robot capable of disassembling iPhones into their individual components. Liam uses advanced sensors and machine learning algorithms to identify and separate components, further enhancing material recovery rates.
- Apple’s Battery Recycling Facility: In 2018, Apple opened its own battery recycling facility in the Netherlands. This facility utilizes innovative technologies to extract cobalt, lithium, and nickel from lithium-ion batteries, enabling the recovery of critical materials for future battery production.
These technological advancements have significantly improved Apple’s ability to recycle lithium-ion batteries responsibly. The company has demonstrated its commitment to developing sustainable solutions that minimize environmental impact and promote a circular economy.
Collaborating for Impact: Partnerships and Industry Initiatives
Apple’s commitment to sustainable battery recycling extends beyond its own operations. The company actively collaborates with industry partners, research institutions, and non-profit organizations to advance the field and create a more circular economy.
Key Highlights:
- Partnership with the World Wildlife Fund (WWF): In 2016, Apple partnered with WWF to promote responsible cobalt sourcing for its batteries. This collaboration aims to address the environmental and social concerns associated with cobalt mining and ensure ethical sourcing practices.
- Collaboration with Universities and Research Institutions: Apple actively engages with universities and research institutions to explore new technologies and solutions for battery recycling. This collaboration fosters innovation and promotes knowledge sharing within the field.
- Support for Industry Initiatives: Apple supports industry initiatives aimed at promoting responsible battery recycling and advancing circular economy principles. The company actively participates in discussions and collaborates with other stakeholders to develop industry standards and best practices.
These partnerships and collaborations demonstrate Apple’s commitment to working collectively to address the challenges of battery recycling. By collaborating with key stakeholders, Apple aims to drive positive change within the industry and contribute to a more sustainable future.
Challenges and Opportunities: Navigating the Path to Circularity
While Apple has made significant strides in its battery recycling efforts, challenges and opportunities remain. The company continues to face hurdles in achieving a truly circular economy for lithium-ion batteries, including:
Challenges:
- Technological Limitations: Current battery recycling technologies are not yet perfect, and further advancements are needed to achieve higher material recovery rates and minimize waste.
- Economic Viability: Recycling lithium-ion batteries can be expensive, and the economic feasibility of scaling up recycling operations remains a challenge.
- Environmental Impact: The extraction and processing of raw materials for battery production can have significant environmental impacts. Finding sustainable alternatives and minimizing these impacts is crucial.
- Consumer Behavior: Encouraging consumers to recycle their old devices and batteries effectively is critical for successful recycling programs.
Opportunities:
- Innovation and Development: Continued investment in research and development can lead to breakthroughs in battery recycling technologies, enabling higher recovery rates and improved environmental performance.
- Collaboration and Partnerships: Working with industry partners, research institutions, and governments can accelerate the development and adoption of sustainable solutions.
- Policy and Regulation: Stronger regulations and incentives can drive innovation and promote responsible battery recycling practices.
- Consumer Engagement: Educating consumers about the importance of battery recycling and providing convenient recycling options can increase participation and drive positive change.
By addressing these challenges and seizing the opportunities, Apple can continue to lead the way in sustainable battery recycling and contribute to a more circular economy.
The Future of Battery Recycling: Apple’s Vision for a Sustainable Tomorrow
Apple’s journey in battery recycling reflects a growing awareness of the environmental impact of electronic devices. The company has demonstrated its commitment to responsible waste management and innovative solutions. While challenges remain, Apple’s vision for a sustainable future is clear:
- Zero Waste: Apple aims to minimize waste and maximize resource recovery, ultimately striving for a zero-waste future.
- Closed Loop: The company envisions a closed-loop system for lithium-ion batteries, where materials are recovered and reused to create new batteries, minimizing the need for new raw materials.
- Circular Economy: Apple’s ultimate goal is to contribute to a circular economy for lithium-ion batteries, where materials are continuously reused and recycled, reducing environmental impact and promoting sustainability.
Apple’s commitment to battery recycling is an important step towards a more sustainable future. By embracing innovation, collaboration, and a circular approach, the company is paving the way for a world where electronic devices are designed for reuse and recycling, minimizing environmental impact and maximizing resource efficiency.
Source:
Apple’s Environmental Responsibility Report
Closure
Thanks for joining us on this journey through Apple’s Battery Recycling Journey: From Closed Loop to Circular Economy. We’ll be back with more content you’ll love.


















