What to Know About Apple’s Data Encryption Policies: A Deep Dive into Privacy and Security
Related Articles
- The Rise Of Siri: How Apple’s AI Revolutionized Voice Recognition
- Unleashing The Power Of Automation: How Apple’s Siri Shortcuts Can Transform Your Daily Routine
- What Apple’s New Developer Tools Mean For App Creators In 2024
- Apple’s Privacy Labels: A Deep Dive Into The App Store’s Transparency Initiative
- Comparing Apple’s 2024 MacBook Lineup: Which Model Is Right For You?
Introduction
If What to Know About Apple’s Data Encryption Policies: A Deep Dive into Privacy and Security has caught your interest, stay with us as we break down everything you need to know.
Video about
What to Know About Apple’s Data Encryption Policies: A Deep Dive into Privacy and Security

Apple has consistently positioned itself as a champion of user privacy, often touting its robust data encryption policies as a key differentiator. But what exactly do these policies entail, and how do they impact your data security? This article delves deep into the world of Apple’s data encryption, exploring its evolution, the various types of encryption employed, and the implications for your digital life.
A History of Encryption: From the Early Days to Modern Practices
Apple’s journey with data encryption has been a gradual progression, mirroring the evolution of encryption technology itself.
The Early Days: A Focus on Device Security (Pre-iOS 4)
In the early days of iOS, Apple’s primary focus was on securing the device itself. This meant encrypting the entire device storage, making it inaccessible to unauthorized users. While effective in protecting against physical theft, this approach offered limited protection for individual data within the device.
The Turning Point: Introducing End-to-End Encryption (iOS 4 and Beyond)
The watershed moment came with the introduction of iOS 4 in 2010. This version marked the beginning of Apple’s commitment to end-to-end encryption, a paradigm shift in data security. End-to-end encryption ensures that only the sender and the intended recipient can access the data, with no third party, including Apple itself, having access to its contents.
This change was a significant step forward, offering users a much higher level of privacy and control over their data. It also set the stage for Apple’s subsequent advancements in data encryption.
The Continued Evolution: Expanding Encryption Coverage
Since iOS 4, Apple has consistently expanded the scope of its encryption policies. This has included:
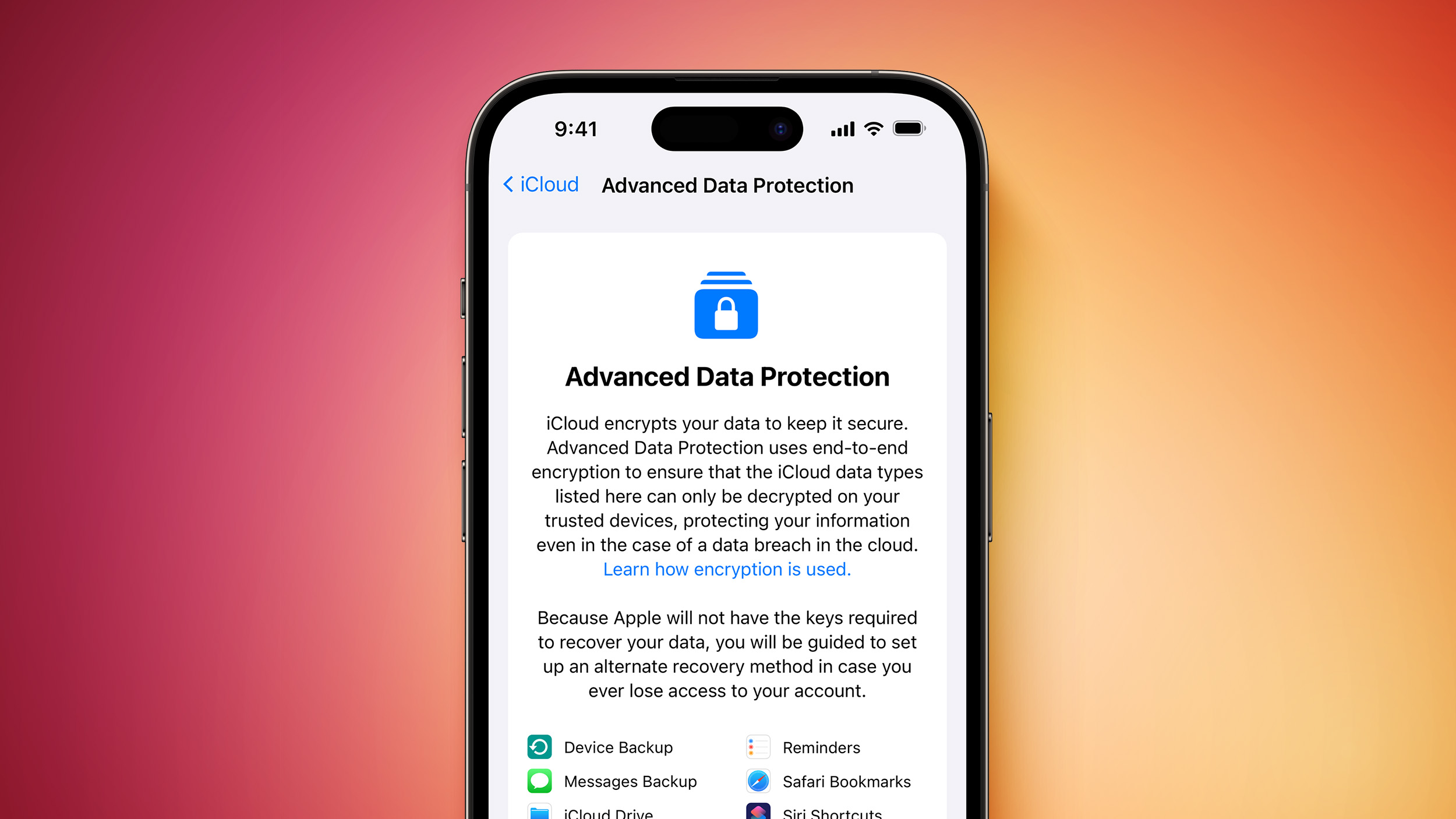
- iCloud Keychain: Protecting passwords and other sensitive information stored in iCloud.
- iCloud Drive: Encrypting files stored in iCloud Drive, ensuring they remain secure even if your device is lost or stolen.
- iMessage and FaceTime: Ensuring secure communication by encrypting messages and calls.
- Safari: Protecting user data, including browsing history and cookies, by encrypting web traffic.
- Health Data: Encrypting sensitive health data, such as medical records and fitness information, stored on your device and in iCloud.
These advancements have solidified Apple’s position as a leader in data privacy and security.
Understanding the Different Types of Encryption: A Breakdown
Apple utilizes a variety of encryption techniques to protect your data. Here’s a breakdown of the most prominent types:
1. Device Encryption: Securing the Entire Device
Device encryption is the cornerstone of Apple’s security strategy. It encrypts the entire storage of your iPhone, iPad, or Mac, making the device inaccessible to anyone without the correct passcode or password.
- How it works: Device encryption uses a complex algorithm to scramble the data on your device. This scrambled data is then stored alongside a unique encryption key, which is protected by your passcode.
- Benefits: Prevents unauthorized access to your data in case of physical theft or loss.
- Limitations: Does not protect individual data stored in cloud services.
2. End-to-End Encryption: Protecting Data in Transit and at Rest
End-to-end encryption is the gold standard for data security. It ensures that only the sender and the intended recipient can access the data, with no third party, including Apple, having access to its contents.
- How it works: The data is encrypted on the sender’s device using a unique key. This key is then used to decrypt the data only on the recipient’s device.
- Benefits: Offers the highest level of privacy and security, protecting data from interception and unauthorized access.
- Examples: iMessage, FaceTime, iCloud Keychain, iCloud Drive.
3. Data in Transit Encryption: Protecting Data During Transmission
Data in transit encryption protects data as it travels between your device and Apple’s servers. This ensures that your data is not intercepted and read by unauthorized individuals during transmission.
- How it works: Data is encrypted using a secure protocol like TLS (Transport Layer Security) before being sent over the internet.
- Benefits: Prevents eavesdropping and data theft during transmission.
- Examples: All communication with Apple services, including iCloud, App Store, and iTunes.
4. Data at Rest Encryption: Protecting Data When Stored
Data at rest encryption protects data when it is stored on Apple’s servers. This ensures that even if Apple’s servers are compromised, your data remains secure.
- How it works: Data is encrypted using a strong encryption algorithm and stored with a unique encryption key.
- Benefits: Prevents unauthorized access to data even if servers are compromised.
- Examples: iCloud Drive, iCloud Keychain, Health data.
Exploring the Implications of Apple’s Encryption Policies
Apple’s robust encryption policies have significant implications for your digital life, both positive and negative.
Advantages: Enhanced Privacy and Security
- Data Protection: Your data is protected from unauthorized access, even in case of device loss, theft, or server breaches.
- Privacy Control: You have control over your data and who can access it, ensuring your privacy is respected.
- Reduced Risk of Hacking: Encryption makes it much harder for hackers to access and steal your data.
- Compliance with Regulations: Apple’s encryption practices align with global data privacy regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA.
Challenges: Law Enforcement Access and User Convenience
- Law Enforcement Access: Encryption can make it difficult for law enforcement to access data for criminal investigations. This has been a point of contention between Apple and authorities, raising questions about the balance between privacy and security.
- User Convenience: Encryption can sometimes create challenges for users, such as the need to remember complex passcodes or the inability to access data on a lost device without a backup.
- Data Recovery: Recovering encrypted data can be difficult if you lose your passcode or forget your encryption key.
The Future of Encryption: A Continuous Evolution
Apple continues to invest in and refine its encryption technologies, constantly seeking to improve data security and privacy. Future advancements might include:
- Improved Key Management: More robust and user-friendly methods for managing encryption keys.
- Enhanced Security Features: New security features that further strengthen data protection.
- Zero-Trust Architecture: A shift towards a more secure and decentralized approach to data storage and access.
- AI-Powered Security: Utilizing artificial intelligence to detect and prevent security threats.
Conclusion: A Commitment to Privacy and Security
Apple’s data encryption policies represent a commitment to user privacy and security, offering a high level of protection for your data. While there are challenges, the benefits of robust encryption far outweigh the drawbacks. By understanding the different types of encryption and their implications, you can make informed decisions about your data security and privacy. As technology evolves, Apple will likely continue to refine its encryption practices, ensuring that your data remains secure in the digital age.
Source:
Closure
We hope this article provided you with valuable insights into What to Know About Apple’s Data Encryption Policies: A Deep Dive into Privacy and Security. Stay tuned for more updates and tips!


















